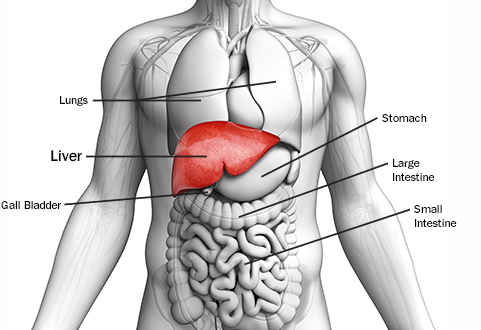
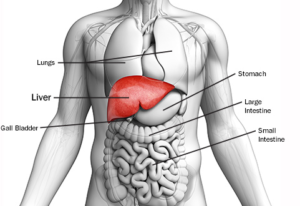
Causes of Hepatitis
World over today, hepatitis has because a term of serious health concern. Hepatitis is a term which generally refers to inflammation of the liver. The cause of hepatitis could be infectious (ie, viral, bacterial, fungal, and parasitic organisms) or can also be noninfectious (eg, alcohol, drugs, autoimmune diseases, and metabolic diseases). Let’s take a look at the major causes of hepatitis.
1. Viral Causes (Viral Hepatitis)
Hepatitis of viral origin simply known as viral hepatitis, accounts for more than 50% of cases of acute hepatitis. The major causes are hepatitis A virus (HAV), hepatitis B virus (HBV), and hepatitis C virus (HCV). Other hepatotropic viruses known to cause hepatitis include hepatitis D virus (HDV) and hepatitis E virus (HEV). Other Infrequent causes of viral hepatitis include Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), adenovirus, cytomegalovirus (CMV), Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), herpes simplex virus (HSV) and adenovirus.
2. Bacterial Causes (Bacterial Hepatitis)
The gastrointestinal tract is colonized by trillions of bacteria and, any injury of the gut barrier causes their translocation to liver and pathogenesis, directly or indirectly. Bloodstream bacterial infection and severe sepsis results in hepatic ischemia or acute hepatitis. Some of the bacteria that have been implicated in cases of hepatitis are Brucella abortus, Bartonela henselae, Coxiella bornetti, Leptospirai nterrogans, Yersinia pestis, Treponema pallidus
3. Parasitic Causes (Parasitic Hepatitis)
Parasitic infections of the liver can also lead to hepatitis. Among the protozoans, Trypanosoma cruzi, Leishmania species, and the malaria-causing Plasmodium species can all cause hepatitis. Another protozoan, Entamoeba histolytica, causes hepatitis with distinct liver abscesses.
Among the worms, the cestode Echinochocus granulosus, also known as the dog tapeworm, infects the liver and forms characteristic hepatic hydatid cysts. The liver flukes Fasciola hepatica and Clonorchis sinensis live in the bile ducts and cause progressive hepatitis and liver fibrosis.
4. Fugal Causes (Fungal Heapatitis)
The liver can be affected by many fungal infectious agents. Many a time, fungal infections are commonly limited to patients that are immunosuppressed. Some common fungal infections found in liver biopsies include Histoplasma, Candida, and Aspergillus. Other fungal infections that may also appear as a result of wide spread (disseminated) disease are Cryptococcus, Blastomyces, and Coccidioides.
5. Alcoholic Hepatitis
The main cause of alcoholic liver hepatitis is frequent, heavy consumption of alcohol. The liver breaks down alcohol for removal from the body. However, the liver can only process alcohol in small doses. Drinking more alcohol than the body can process may cause injury or serious damage to the liver leading to alcoholic hepatitis. The infection can be mild or severe. The person may need a liver transplant if they do not receive treatment or stop consuming alcohol during the early stages.
6. Drug Induced Hepatitis
Usually, drug-induced hepatitis sets in as redness and swelling of the liver resulting from harmful or toxic amount of some medicines, vitamins, herbal remedies, or food supplements. The liver helps to break down certain medicines in the blood. If there is too much medicine in the blood for the liver to break down, the liver can become badly damaged. This can lead to drug-induced hepatitis.
Many types of medicines may cause drug-induced hepatitis. These include:
- Pain and fever medicines that have acetaminophen can cause hepatitis
- Anabolic steroids, man-made medicines that are like the male sex hormone testosterone can cause hepatitis
- Some medicines used to treat bacterial infections (antibiotics) can also cause hepatitis
- Aspirin and over-the-counter pain and fever medicines (NSAIDs or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medicines) can also cause hepatitis
- Birth control pills (oral contraceptives) can cause hepatitis
- Statins, used to lower cholesterol can also cause hepatitis
- Sulfa medicines, a type of antibiotic can cause hepatitis
- Anti-epileptic medicines
- Herbal medicines can also cause hepatitis. It is worthy to note that not all “natural” or “herbal” supplements are safe. They are also not regulated for safety.
7. Autoimmune Hepatitis
The body’s immune system was configured to normally attacks viruses, bacteria and other pathogens. Autoimmune hepatitis however occurs when the body’s immune system targets the liver instead. This attack on the liver can lead to chronic inflammation and serious damage to liver cells. The reason why the body turns against itself is unclear, but researchers think autoimmune hepatitis could be caused by the interaction of genes controlling immune system function and exposure to particular viruses or drugs.
8. Metabolic Hepatitis
Metabolic liver disease is strongly associated with metabolic syndrome, obesity, insulin resistance and diabetes, and hypertriglyceridemia. Over time, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease can progress to non-alcoholic steatohepatitis, which additionally involves liver cell death, liver inflammation and possible fibrosis. Factors accelerating progression from NAFLD to NASH are obesity, older age, non-African American ethnicity, female gender, diabetes mellitus, hypertension, higher ALT or AST level, higher AST/ALT ratio, ultrasound steatosis score and low platelet count.
Conclusion
Hepatitis can be occur as a result of any of the above factors. Although hepatitis is commonly caused by a viral infection, there are other possible causes of hepatitis. Because of many critical functions performed by the liver that affect metabolism. It is important to confirm the exact cause of hepatitis whenever it sets in and treat accordingly.
 Healthveli
Healthveli